Ear syringing is a common procedure used to remove excess earwax and alleviate ear blockage. It involves the use of a syringe to flush warm water into the ear canal, dislodging and washing away accumulated earwax.
While ear syringing can be effective for many individuals, it is essential to understand its safety, potential risks, and who should avoid this procedure.
This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of ear syringing, its safety, and when it is appropriate to seek professional ear cleaning services.
The experienced audiologists at The Hearing Space offer ear cleaning tips in this post as well as safe and effective ear cleaning, addressing any earwax buildup or hearing concerns.
Understanding Ear Syringes
An ear syringe is a medical device specifically designed for ear irrigation. It typically consists of a syringe-like mechanism with a soft, rubber bulb or a flared tip to facilitate safe and controlled water flow into the ear canal.
Ear syringes are available over the counter and are often used for at-home ear cleaning.
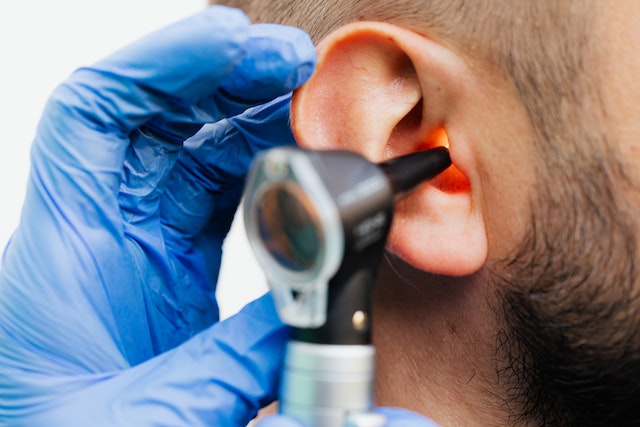
How Ear Syringes Work
Ear syringing works by gently flushing warm water into the ear canal, which helps soften and dislodge earwax.
The force of the water dislodges the earwax, allowing it to be washed out of the ear canal.
This process can be effective in clearing excess earwax and relieving ear blockages.
Benefits of Ear Syringing
Ear syringing offers several benefits, including:
Effective Earwax Removal:
Ear syringing can be effective in removing excess earwax that has built up in the ear canal.
Alleviating Ear Blockage:
The removal of earwax through syringing can alleviate ear blockages and improve hearing.
Quick Procedure:
Ear syringing is generally a quick procedure that can be performed in a doctor’s office or at home.
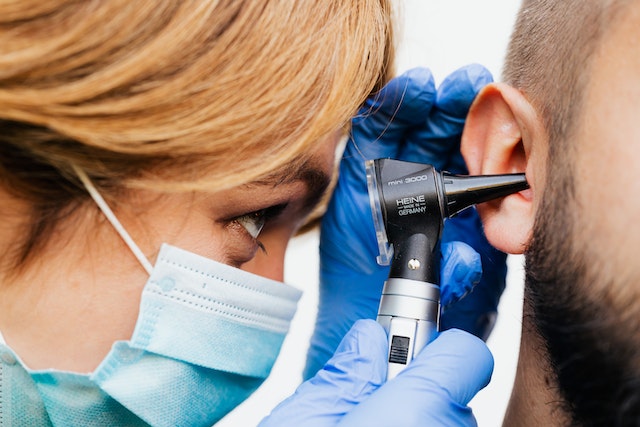
Potential Risks and Precautions
While ear syringing can be beneficial, it also carries potential risks and requires proper precautions. Some of the risks include:
1. Ear Canal Injury:
Incorrect use of an ear syringe or excessive water pressure can cause injury to the delicate ear canal.
Ear Infection:
Ear syringing may increase the risk of ear infections, especially if the ear canal is already compromised.
Pushing Earwax Deeper:
In some cases, ear syringing can inadvertently push earwax deeper into the ear canal, worsening the blockage.
It is crucial to exercise caution when using ear syringes and to follow the manufacturer’s instructions or the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Who Should Avoid Ear Syringing?
Not everyone is a suitable candidate for ear syringing. Individuals with the following conditions should avoid this procedure:
History of Ear Infections:
Those with a history of recurrent ear infections or chronic ear conditions should avoid ear syringing, as it may exacerbate the problem.
Tympanic Membrane Perforation:
If there is a perforation or hole in the eardrum, ear syringing is not recommended, as it can cause further damage.
Narrow Ear Canal:
Individuals with a naturally narrow ear canal may be at a higher risk of injury during ear syringing.
Alternatives to Ear Syringing
For individuals who are not suitable candidates for ear syringing or prefer alternative methods, there are several options for earwax removal, including:
Ear Drops:
Over-the-counter ear drops can be used to soften earwax, making it easier to remove naturally or during professional ear cleaning.
Ear Irrigation by a Healthcare Professional:
Seeking ear irrigation performed by a trained healthcare professional ensures safe and effective earwax removal.
Manual Ear Cleaning by a Professional:
A healthcare professional can manually remove earwax using specialized instruments if necessary.
The Importance of Professional Ear Cleaning
While ear syringing can be performed at home, professional ear cleaning by audiologists or ENT specialists offers many advantages. These professionals have the expertise and tools to safely and effectively remove excess earwax without risking injury or infection.
Additionally, they can address any ear-related concerns and provide personalized advice on ear hygiene.
Conclusion
Ear syringing can be an effective method for removing excess earwax and alleviating ear blockages. However, it is essential to approach this procedure with caution and follow the necessary precautions to avoid potential risks. Not everyone is a suitable candidate for ear syringing, and those with specific ear conditions should avoid it. It is advisable to consult a suitable professional in the healthcare, particularly an audiologist or ENT specialist, before attempting ear syringing at home.































